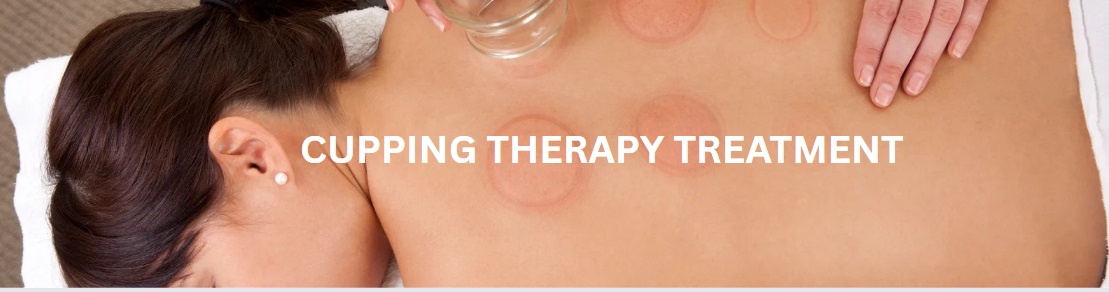
What is Cupping Therapy Treatment
Cupping therapy, an ancient healing modality, involves placing cups on the skin to create suction. This suction draws up the skin and superficial muscle layer, promoting blood flow, reducing inflammation, and fostering relaxation. While its precise origins are debated, evidence suggests its practice in ancient Egypt, China, and the Middle East, highlighting its long-standing role in traditional medicine systems.
The practice of cupping therapy has evolved over centuries, resulting in various techniques. Dry cupping, the most common method, involves placing heated or air-pumped cups on the skin. Traditionally, heat was used to create a vacuum within glass cups. Modern practitioners often employ plastic cups with valves and a handheld pump to achieve the desired suction level. Cups are typically left in place for 5 to 10 minutes.
Another variation is wet cupping, which involves making small, superficial incisions on the skin before applying the cups. The suction then draws out a small amount of blood. This technique is believed to remove toxins and stagnant blood from the body, although scientific evidence supporting this claim is limited. Wet cupping is less common than dry cupping and requires strict adherence to hygiene and safety protocols to prevent infection.
Moving cupping involves applying oil to the skin and then gliding the suctioned cups across a specific area. This technique is often used to address larger muscle groups and can feel similar to a deep tissue massage. The gliding motion helps to further increase blood flow and release muscle tension.

The effects of cupping therapy are multifaceted. The suction created by the cups increases blood circulation to the treated area. This enhanced blood flow can help deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues, while also facilitating the removal of metabolic waste products. Many individuals report a reduction in muscle tension and pain following cupping sessions. The gentle pulling sensation can help to release adhesions in muscles and fascia, improving flexibility and range of motion.
Furthermore, cupping therapy is often associated with a sense of relaxation and well-being. The parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for the “rest and digest” response, can be stimulated by the treatment, leading to a decrease in stress and anxiety. Some proponents also suggest that cupping can influence the lymphatic system, aiding in detoxification and immune function, although more research is needed in this area.
The tell-tale circular marks left by cupping are a common and temporary side effect. These marks, which can range in color from light pink to dark purple, indicate the degree of stagnation and blood flow in the area. They are generally painless and typically fade within a few days to a couple of weeks. Other potential but less common side effects include mild bruising, soreness, or skin irritation around the cup margins.
While cupping therapy has gained popularity in recent years, it’s essential to approach it with realistic expectations and consult with a qualified and licensed practitioner. A thorough assessment of an individual’s health history and current condition is crucial to determine if cupping is appropriate and to tailor the treatment accordingly. Cupping therapy should not be considered a substitute for conventional medical treatment, especially for serious health conditions. However, when used as a complementary therapy, it can be a valuable tool for managing pain, reducing muscle tension, and promoting relaxation for some individuals. Ongoing research continues to explore the mechanisms and effectiveness of cupping therapy for various health concerns